Original Article
Relationship Between Forward Head Posture and Hand Function in Middle-Aged Tailors: A Cross-Sectional Study
Praveen Baby, Manju Unnikrishnan, Remya N, Fathima A, Jesna Jeny Nellissery, Ninu Antu Menachery
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.
Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy Journal 18(3):p 223-228, July-Sep 2025. | DOI: 10.21088/potj.0974.5777.18325.5
How Cite This Article:
Baby P, Unnikrishnan M, Remya N, et al. Relationship Between Forward Head Posture and Hand Function in Middle-Aged Tailors: A Cross-Sectional Study. Physio Occup Ther J. 2025;18(3):223-228.Timeline
Abstract
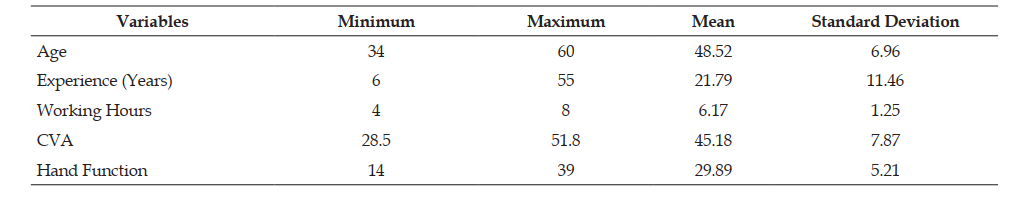
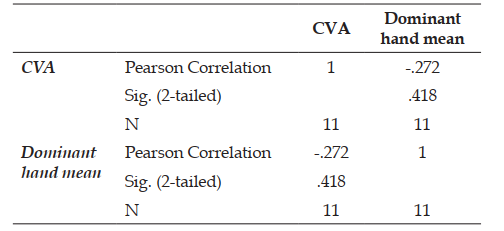
Background of the study: Tailors are creative workers who stitch clothing and have exceptional machine and hand abilities. These employees who operate in a hunched posture for extended periods of time impair tension, stretching and ligaments around neck. Reduced hand function in tailors may be caused by forward head posture during sewing. Objective: To find the association between forward head posture and hand function in tailors. Methods: The cross-sectional study was conducted on 29 subjects aged between 40–65 years, who met with inclusion criteria. Based on the experience, the subjects were grouped into three classes of Skilled tailors, Expert tailors, and Master tailors. The forward head posture and hand function were assessed by craniovertebral angle [CVA] and nine-hole peg test [NHPT] respectively. The obtained data was statistically evaluated to find out whether forward head posture was correlated with hand function in tailors. Results: The mean scores obtained for CVA and Hand Function were 45.18 ± 7.87, 29.89 ± 5.21, respectively. Pearson correlation coefficient was computed to assess the correlation between the obtained variables among skilled, expert and master tailors. The obtained correlational values were [r = -0.244] in skilled tailors and [r = -0.272] in expert tailors, whereas a weak positive correlation [r = 0.279] in master tailors. This shows there was no significant correlation between hand function and forward head posture in tailors. Conclusion: The study concluded that there was no correlation between forward head posture and hand function in tailors.
References
- 1. Sugianto DK, Rahmanto S, Irawan DS. The relationships between sewing and forward head posture. ptji 2020;1(1):9–12.
- 2. Anwar, N., Riaz, H., Saeed, A., & Ashraf, F. 2020. Frequency of work related musculoskeletaldisorders and ergonomic risk assessments among tailors. JPMA. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association, 70(12(A)), 2164–2167.
- 3. Shaghayeghfard B, Ahmadi A, Maroufi N, Sarrafzadeh J. Correction to: Evaluation of forward head posture in sitting and standing positions. Eur Spine J 2021;30(10):3135.
- 4. Fayez, E. S. 2014. The correlation between neck pain and hand grip strength of dentists. Occupational Medicine & Health Affairs, 02(05)10.4172/2329.
- 5. Rosenblum S, Josman N. The relationship between postural control and fine manual dexterity. Phys Occup Ther Pediatr 2003;23(4):47–60.
- 6. Jain S, Galgotias University, Greater Noida. Correlation of neck posture with hand function in computer professionals. J med sci clin res 2018;6(6).
- 7. Feys P, Lamers I, Francis G, Benedict R, Phillips G, LaRocca N, et al. The Nine Hole Peg Test as a manual dexterity performance measure for multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 2017;23(5):711–20.
- 8. Chansirinukor W, Wilson D, Grimmer K, Dansie B. Effects of backpacks on students: measurement of cervical and shoulder posture. Aust J Physiother 2001;47(2):110–6.
- 9. Salahzadeh Z, Maroufi N, Ahmadi A, Behtash H, Razmjoo A, Gohari M, et al. Assessment of forward head posture in females: observational and photogrammetry methods. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil 2014;27(2):131–9.
- 10. Johansson GM, Häger CK. A modified standardized nine hole peg test for valid and reliable kinematic assessment of dexterity post-stroke. J Neuroeng Rehabil.
- 11. Alshahrani A, Samy Abdrabo M, Aly SM, Alshahrani MS, Alqhtani RS, Asiri F, et al. Effect of smartphone usage on neck muscle endurance, hand grip and pinch strength among healthy college students: A crosssectional study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021;18(12):6290.
- 12. Wessel J. The effectiveness of hand exercises for persons with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. J Hand Ther 2004;17(2):174–80.
- 13. Mosaad DM, Abdel-aziem AA, Mohamed GI, Abd-Elaty EA, Mohammed KS. Effect of forward head and rounded shoulder posture on hand grip strength in asymptomatic young adults: a cross-sectional study. Bull Fac Phys Ther 2020;25(1).
Data Sharing Statement
Funding
Author Contributions
Ethics Declaration
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
About this article
Cite this article
Baby P, Unnikrishnan M, Remya N, et al. Relationship Between Forward Head Posture and Hand Function in Middle-Aged Tailors: A Cross-Sectional Study. Physio Occup Ther J. 2025;18(3):223-228.
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.
| Received | Accepted | Published |
|---|---|---|
| May 15, 2025 | June 21, 2025 | September 28, 2025 |
DOI: 10.21088/potj.0974.5777.18325.5
Keywords
Forward head postureHand functionCranio-vertebral angleHand gripSearch for Similar Articles
Similar Articles
- Exploring the Connection Between Stress, Anxiety, and Central Pain Mechanisms
- Comparative Effectiveness of Mulligan SNAGs and the McKenzie Method in the Mana...
- To Compare the Effectiveness of Dual Task Training Versus Task Oriented Circuit...
- Role of Virtual Reality in Physiotherapy
- Normative Values of One Leg Stance in Urban Adults of 20-40 Years
Article Level Metrics
Last UpdatedSaturday 28 February 2026, 04:14:17 (IST)
Accesses
Citations
Download citation
Article Keywords
Keyword Highlighting
Highlight selected keywords in the article text.
Timeline
| Received | May 15, 2025 |
| Accepted | June 21, 2025 |
| Published | September 28, 2025 |
licence
This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.