Original Article
Simultaneous Determination and Method Validation For Opioids, Cannabinol and Nicotine in Postmortem Whole Blood Using High Performance thin Layer Chromatography Mass Spectrometry
Pallavi Choudhary, Kanak Lata Verma, Lijo T. Varghese, A. K. Jaiswal, Adarsh Kumar
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.
Red Flower's Journal of Forensic Chemistry and Toxicology 11(1):p 7-15, Jan-June 2025. | DOI: 10.21088/jfct.2454.9363.11125.1
How Cite This Article:
Choudhary P, Verma KL, Varghese LT, et al. Simultaneous Determination And Method Validation For Opioids, Cannabinol and Nicotine in Postmortem Whole Blood Using High -Performance thin Layer Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. J Forensic Chemistry Toxicol. 2025;11(1):7–15.Timeline
Abstract
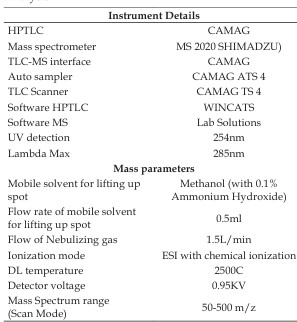
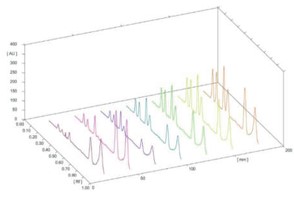
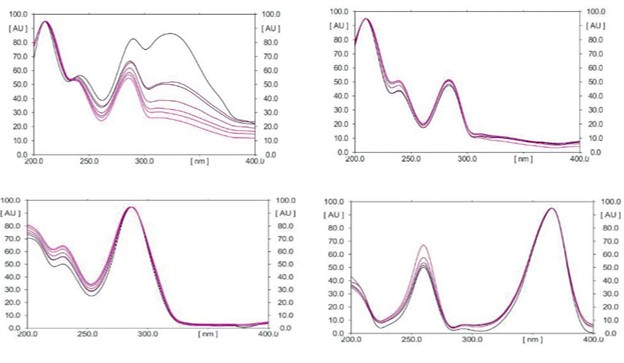
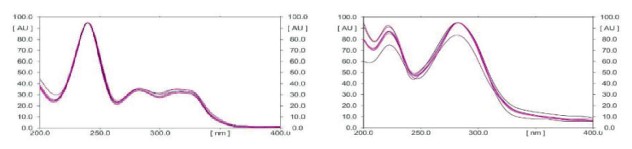
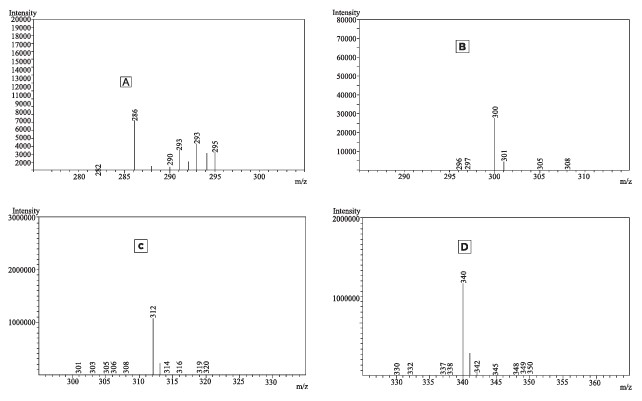
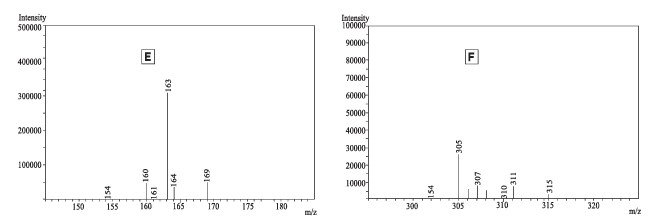
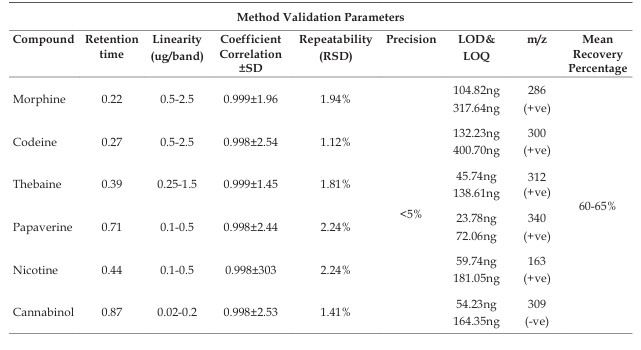
Background: Opioids, cannabis and nicotine are the oldest and highly abused substancesglobally.Thedetectionandidenti cationof thesedrugs isamajor challenge for the law enforcement agencies as well as forensic chemists, especially when the cases pertain to sexual assaults/drug-facilitated sexual assaults. Aim: To develop a determination method which can quantify opioids, cannabinol and nicotine simultaneously in whole blood. Objective: Thispaper presents avalidatedmethod for the identi cationand quantitation of Morphine (MOR), Codeine (COD), Thebaine (THB), Papaverine (PAPA), Cannabinol (CBN) & nicotine (NIC) using High performance thin layer chromatography- Mass spectrometry HPTLC-MS, from whole blood at postmortem. Material & Method: Quantitative analysis of MOR, COD, THB, PAPA, CBN and NIC were done using HPTLC and MS was operating in selective ion-monitoring mode for accurate identifiation of the drugs under study. Small Volume Liquid extraction (SVLE) technique using ethyl acetate-hexane (80:20) were used for the extraction of blood. Pre-coated HPTLC (silica gel G 60 F254) plates were developed using mobile phase ethyl acetate: methanol: ammonia (8.5:1:0.5). Result: The screening of HPTLC plates was done by UV light and the m/z ratio of drugs was obtained by lifting spots from plates using the HPTLC-MS interface. Method validation was done according to the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) guidelines. The technique will encourage forensic chemists to embrace the validated HPTLC-MS method. Conclusion: The developed HPTLC-MS method is simple, sensitive, precise, accurate, economic and can be used for quantitative analysis of MOR, COD, THB, PAPA, NIC and CBN in blood.
References
- 1. Sharma B, Arora A, Singh K, Singh H, Kaur P. Drug Abuse: Uncovering the Burden in RuralPunjab. JFamilyMedPrimCare. 2017; 6(3):558-562.
- 2. KulsudjaritK.DrugprobleminSoutheastand Southwest Asia. Ann.N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2004; 1025:446-457.
- 3. Huffman A. Controlling Opioid Abuse in the Emergency Department. Annals of Emergency Medicine. 2013; 61(6):A13-A15.
- 4. Bridgeman MB, Abazia DT. Medical Cannabis History, Pharmacology & Implications for the Acute Care Setting. Pharmacy & Therapeutics. 2017; 42(3):180-188.
- 5. Biological Process Underlying Co-Use of Alcohol & Nicotine: Neuronal Mechanism, Cross-Tolerance & Genetics Factors. https:// pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/arh293/186 192.htm. Accessed on 01/05/2023.
- 6. TheOpium Alkaloid. https://www.unodc. org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/bulletin/ bulletin-1953-01-01-3-page005.html. Accessed on 01/05/2023.
- 7. Green TC, Park JN, Gilbert M, McKenzie M, Struth E, Lucas R, Clarke W, Sherman SG. An assessment of the limits of detection, sensitivityandspeci cityof threedevicesfor public health-based drug checking of fentanyl in street-acquired samples. International Journal of Drug Policy.2020;77:102661:https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.drugpo.2020.102661.
- 8. Gilbert N, Antonides L.H, SchoÒeld C.J., et al. Hitting the Jackpot – development of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC MS) and other rapid screening methods for the analysis of 18 fentanyl– derived synthetic opioids. Drug Testing and Analysis.2020; 12(6) 798-811.
- 9. Shende C, Farquharson A, Brouillette C, Smith W, Farquharson S. Quantitative Measurements of Codeine and Fentanyl on a SurfaceEnhanced Raman-Active Pad.Molecules. 2019; 24(14): 2578.
- 10. Liu L , Wheeler S. E ,Venkataramanan R, Rymer J. A, Pizon A.F. , Lynch M.J., Tamama K.Newly Emerging Drugs of Abuse and Their Detection Methods, An ACLPS Critical Review. Am J Clin Pathol.2018;149:105-116
- 11. Sharma P, Murthy P, Bharath MMS. Chemistry, Metabolism and Toxicology of Cannabis: clinical Implications. Iranian Journal of Psychiatry.2012; 7(4):149-156.
- 12. Drug Market Trends Cannabis Opioids. https://www.unodc.org/res/wdr2022/ MS/WDR22_Booklet_3.pdf Accessed on 30/04/2023.
- 13. Magnitude of Substance Use in India 2019. socialjustice.nic.in/writereaddata/upload le/ magnitude-substance-use-India-Reportpdf. Accessed on 30/04/2023.
- 14. Cannabis-and-Opium-based-drugs Cheapest in India. https://timeso ndia.indiatimes. com/indian-drugs-cheapest-in articlesshow/59230170cms. 30/04/2023. theworld/ Accessed on
- 15. Sheehan T.J, Hamnett H.J, BeasleyR, Fitzmaurice P.S. Chemical and physical variations of cannabis smoke from a variety of cannabis samples in New Zealand. Forensic Sciences Research. 2019; 4 (2):168–178.
- 16. Verma KL, Kumar M, Singh AP. HPTLC MS as a Neoteric Hyphenated Technique for SeparationandForensic Identi cationof Drugs. Journal of analytical, Methods and Instrumentation. 2018; 8:1-5.
- 17. Ala A. Alhusban, Samah A. Ata .Simple HPLCmethod for rapid quanti cation of nicotine content in e-cigarettes liquids. Acta Chromatographica, 10.1556/1326.2020.00832 2020, DOI: https:// akjournals.com/view/journals/1326/ aop/article-10.1556-1326.2020.00832/ article-10.1556-1326.2020.00832.xml (accessed on 30.04.2023)
- 18. Chan KW, Harun H. Method Validation for theIdenti cationofNicotineinVapesbyGC MS.Kimia Science Communication Magazine . 2019; 42(2).(accessed on 30.04.2023)
- 19. Tobacco use Causes 1 Death Every 6 seconds. https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/ city/nagpur/5891475.cms. Accessed 30/04/2023
- 20. Smoking & Tobacco Use. https://www. cdc.gov/tobacco/basic-information/health effects/index.htm. Accessed on 30/04/2023.
- 21. Validation of analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology Q2(R1). https://www.ich.org/ home.html. Accessed on 30/04/2023.
- 22. Rao MS Toxicological Manual, Directorate of Forensic Science, Ministry of Home Affairs Government of India, New Delhi, (2005) 1st Edn.SelectiveandScienti cBooks.
- 23. Meng P, Wang Y. Small Volume Liquid Extraction of Amphetamines in Saliva. Forensic Science International.2010; 197(1-3):80-4.
- 24. Clark’s Analysis of Drugs and Poison 3rd edition Pharmaceutical Press 2005.
- 25. JugU,GlavnikV,KranjcE,VovkI.HPTLC Densitometric & HPTLC-MS Methods for analysis of Flavonoids. Journal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies 2018; 41(6):329-341.
Data Sharing Statement
Funding
Author Contributions
Ethics Declaration
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhary P, Verma KL, Varghese LT, et al. Simultaneous Determination And Method Validation For Opioids, Cannabinol and Nicotine in Postmortem Whole Blood Using High -Performance thin Layer Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. J Forensic Chemistry Toxicol. 2025;11(1):7–15.
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.
| Received | Accepted | Published |
|---|---|---|
| May 15, 2025 | May 05, 2025 | June 12, 2025 |
DOI: 10.21088/jfct.2454.9363.11125.1
Keywords
HPLTC-MSOpioidsNicotineCannabinolForensic ScienceSearch for Similar Articles
Similar Articles
- H-NMR based Metabolic Fingerprinting in Forensic Investigations
- Sudden Death Due to 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Cardiotoxicity in a Case of Esophagea...
- Boerhaave Syndrome Masquerading as Sudden Death: A Virtual Autopsy Perspective
- Planned Complex Suicide Involving Phenyl Ingestion and Hanging: A Medico-Legal...
- A Fatal Journey of a Clot: Pulmonary Thromboembolism Case Report
Article Level Metrics
Last UpdatedMonday 26 January 2026, 20:33:58 (IST)
Accesses
Citations
Download citation
Article Keywords
Keyword Highlighting
Highlight selected keywords in the article text.
Timeline
| Received | May 15, 2025 |
| Accepted | May 05, 2025 |
| Published | June 12, 2025 |
licence
This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.