Original Article
Effect of STP on First Aid Management and Prevention for Chocking in Children
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator
RFP Journal of Hospital Administration 8 (2):p 55-59, July-December 2024. | DOI: NA
How Cite This Article:
Sanas SV. Effect of STP on first aid management and prevention for choking in children. RFP J Hosp Adm. 2024;8(2):55-9.Timeline
Abstract
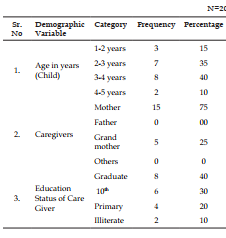
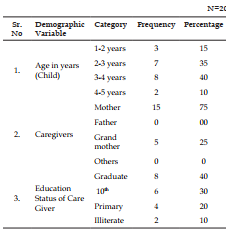
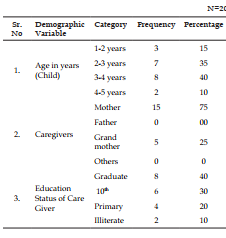
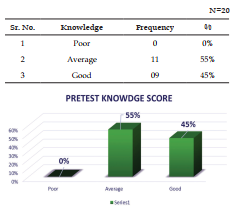
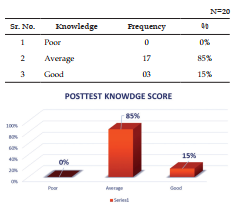
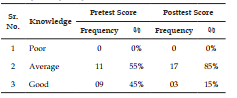
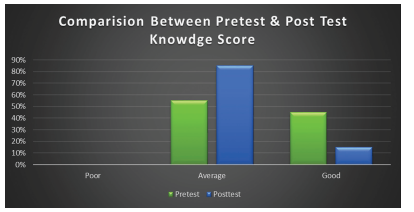
The present study was Effectiveness of structure teaching programme on knowledge regarding first aid management and prevention for chocking in children among caregivers of under five children. Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness of structure teaching programme on knowledge regarding first aid management and prevention for choking in children among caregivers of under five children at selected rural areas. Methodology: Research, Design-experimental descriptive design, sampling technique- Purposive sampling, Research Setting- selected Community areas Result: Here we can discuss about the effectiveness of structure teaching programme on knowledge regarding first aid management and prevention for chocking in children among caregivers of under five children as per set the criteria for poor, average and good. With regard to scores, 0 (0%) care giver had poor knowledge, 11 (55%) care giver had average knowledge and 9 (45%) care giver had good knowledge in Pretest but after giving the Structure teaching Programme the score was 0 (0%) care giver had poor knowledge, 17 (85%) care giver had average knowledge and 03 (15%) care giver had good knowledge in Post-test.
References
- 1. Kumar, A., Varshney, S., Tyagi, A.K., Patro, S. K., Malhotra, M., & Bhardwaj, A. (2019). Choking-A Public Health Problem-Are We Prepared? Indian Journal of Community Health, 31(2), 284-286.
- 2. Lu, Q. F., Ma, Q., Rithwan, S. M. S., Ng, H. C., Lee, S. L., Lee, K. M., ... & Xie, H. (2017). Risk factors and nursing strategies to manage choking in adults with mental illness: a systematic review protocol. JBI Evidence Synthesis, 15(8), 1998-2003.
- 3. Rimell FL, Thome A, Stool S, Reilly JS, Rider G, Stool D, Wilson CL. Characteristics of objects that cause choking in children. JAMA. 1995 Dec 13;274(22):1763-6.
- 4. Lento M, Maria T. A study to assess the effectiveness of self- module on knowledge regarding selected first aid measures among primary school teachers in Ernakulum district. Into J Medic Heal Profess Res. 2015;2(1):17-20.
- 5. Tint T. Effect of a planned teaching program on knowledge regarding pediatric emergencies and its first aid management among mothers of under-five children in selected anganwadis at Ernakulum district in Kerala. Ind J Res. 2017;6(9):32-4.
- 6. Kernell, J. W., DePaola, R. V., Maglione, A. M., Ahern, L. N., Penney, N. G., & Addiss, D. G. (2018). Risk of adverse swallowing events and choking during deworming for preschool-aged children. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 12(6), e0006578.
- 7. Stanford medicine chlidrens health, foregin body in throat, was first indexed by Google in April 2013.
- 8. Abdelmalik, M., Mohammead, M., Mohammed, A., Abdalla, A., Saeed, A., Sambu, B. and Beraima, M. (2022). Effects of Education Programs on School Students’ Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice Regarding First Aid for a Choking.
- 9. Nabiha gul hassan knowledge of caregivers for the prevention of injuries among Children in day-care centres, in putrajaya and selangor, 2016 international journal for studies on children, women, elderly and disabled, 2016;1(1): 0128- 309x.
- 10. Habeeb, K.A., & Alarfaj, G. (2020): Saudi parents’ awareness regarding burn, choking, and drowning first aid in children. Journal of family medicine and primary care, 9(3),1370.
- 11. IPA, The American Association for the Child’s Right to Play. IPA Declaration of a child, 2007.
- 12. Mohan D, Anderson R. Injury prevention and control: International course on injury prevention and control. TRIPP, New Delhi, 2000.
- 13. D’souza. A study to evaluate the effectiveness of planned teaching programme on knowledge and attitude about complementary feeding among mothers and infants in selected primary health centers of udupi district, Karnata Unpublished Masters of Nursing thesis, Manipal university: 2006.
Data Sharing Statement
Funding
Author Contributions
Ethics Declaration
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
About this article
Cite this article
Sanas SV. Effect of STP on first aid management and prevention for choking in children. RFP J Hosp Adm. 2024;8(2):55-9.
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator
| Received | Accepted | Published |
|---|---|---|
| November 11, 2024 | December 28, 2024 | December 30, 2024 |
DOI: NA
Keywords
Care giverFirst aidPreventionChockingStructure Teaching ProgrammeUnder Five ChildrenCommunitySearch for Similar Articles
Similar Articles
- Role of Fibrinogen Concentrate and Its Effect on Blood Loss in on Pump Cardiac S...
- From Sequencing to Prediction: Leveraging Next Generation Sequencing & Machine L...
- The Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023: Forensic and Medicolegal Implica...
- Perception of “Young Adults” on Integration of Telemedicine in Healthcare Servic...
- Accomplishment of International Patient Safety Goals (IPSG) in Enhancing Patient...
Article Level Metrics
Last UpdatedMonday 26 January 2026, 19:17:32 (IST)
Accesses
Citations
Download citation
Article Keywords
Keyword Highlighting
Highlight selected keywords in the article text.
Timeline
| Received | November 11, 2024 |
| Accepted | December 28, 2024 |
| Published | December 30, 2024 |
licence
This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator