Original Article
To Compare the Effectiveness of the Dry Needling Versus Instrumented Assisted Soft Tisse Mobilization Technique on Scapular Dyskinesia in College Students with Trapezitis: A Comparative Study
Amit S. Patel, Keshvi Ajaykumar Soni
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.
Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy Journal 16(1):p 37-49, January-March 2023. | DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21088/potj.0974.5777.16123.3
How Cite This Article:
Patel AS, Soni KA. To compare the effectiveness of the dry needling versus instrumented assisted soft tissue mobilization technique on scapular dyskinesia in college students with trapezitis – a comparative study. Physiother Occup Ther J. 2023;16(1):37-49.Timeline
Abstract
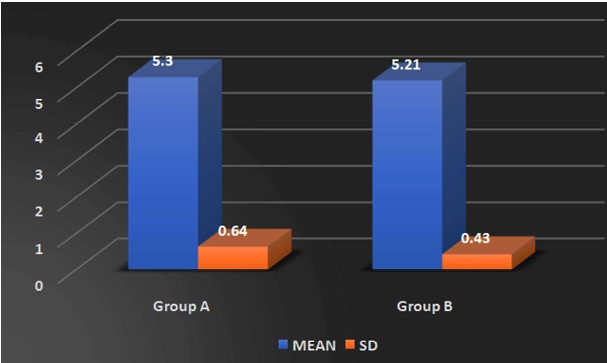
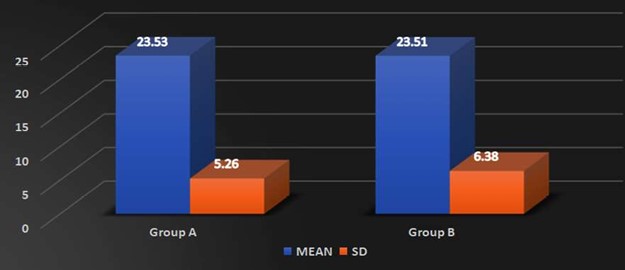
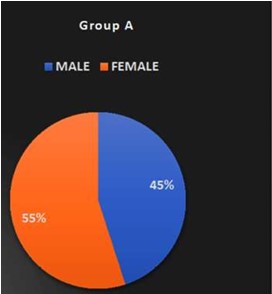
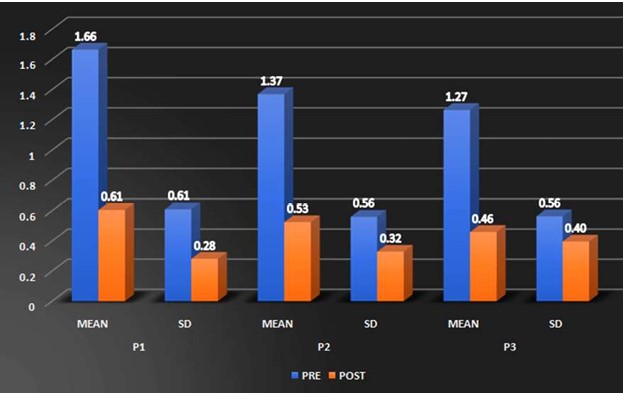
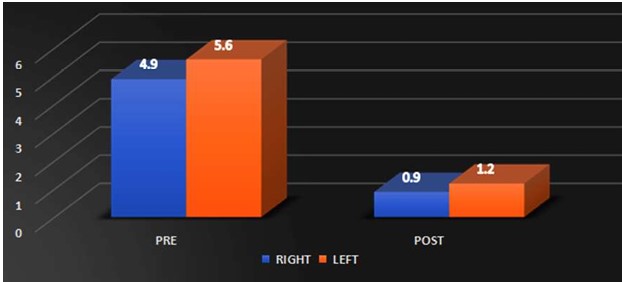
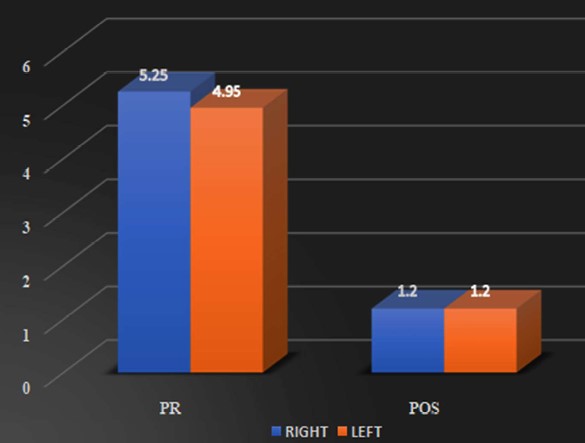
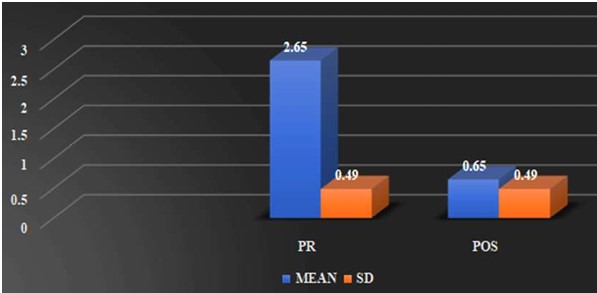
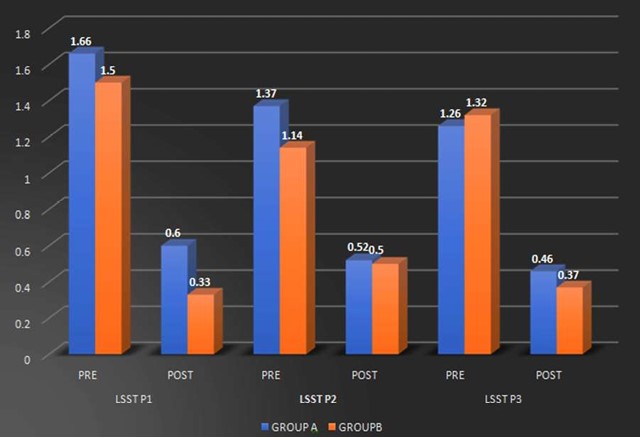
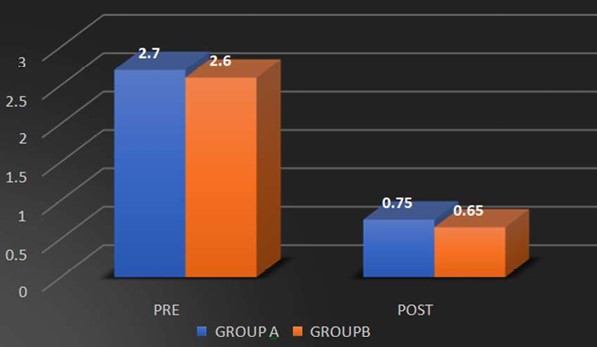
Background: Scapular dyskinesis (‘dys’—alteration of, ‘kinesis’—movement) is a collective term that refers to movement of the scapula that is dysfunctional. The Upper Trapezius (UT) muscle has been found to be often affected by MTrPs. Common symptoms in individuals with MTrPs in the UT muscle include a taut and painful muscle, tension headache, neck pain, dizziness or vertigo, limited neck, and shoulder ROM. The former technique Dry needling is used to treat myofascial trigger points (MTrPs), which are described as localized hypersensitive spots in a palpable taut band of muscle, and the other is Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM) is a popular therapeutic approach for myofascial restrictions. As college students have to carry heavy bag pack, their scapular stabilizer muscle may become weaken due to continuous stress. Hence this study was undertaken to find out the effectiveness of either Dry needling or Instrumented assisted soft tissue manipulation in case of scapular dyskinesia with trapezitis among college students. Purpose of the Study: Aim of the study is to evaluate the effectiveness of Dry Needling versus Instrumented Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization on scapular dyskinesia in college students with trapezitis, and objective is to determine the effect of Dry Needling on Scapular Dyskinesia in college students with Trapezitis, and to determine the effect of Instrumented Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization technique on scapular dyskinesia in college students with Trapezitis, and to compare the effectiveness of Dry Needling versus Instrumented Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization technique on scapular dyskinesia in college students with Trapezitis. Methods: A comparative study was conducted in M.B Gohil Institute of Medical Science and Research Center, College of Physiotherapy, Navsari (OPD) on 40 college students including both male and female of Navsari district based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. Outcome of the study that is Dynamic scapular motion test, Pressure pain threshold scale, Lateral scapular slide test and Numeric pain rating scale were assessed for each college students with prior inform consent form signed by the participant. Comparison of the effectiveness of Dry needling and IASTM Tool was done statistically. Outcome Measure: (1) NPRS (2) Pressure Pain Thresold Scale (3) Dynamic Scapular Motion Test (4) Lateral Scapular Slide Test. Amit. S. Patel, Keshvi Ajaykumar Soni/To Compare the Effectiveness of the Dry Needling Versus Instrumented Assisted Soft Tisse Mobilization Technique on Scapular Dyskinesia in College Students with Trapezitis – A Comparative Study Statistical Analysis: Statistical Analysis was done by using SPSS 20 software. Results: In Study, within group comparisons showed a significant improvement in NPRS, PPTS, LSST of group-a and group-b. p value (<0.005) whereas, in between group there was no significant difference found i.e., Dry needling and instrumented assisted soft tissue mobilization have similar effects on active mayo-facial trigger points of upper trapezius muscle. Conclusion: This study suggests that Dry Needling and soft tissue mobilization with myorelease tool may have similar effects on active trigger points of the upper trapezius muscle, which include reducing the pain intensity, increasing the pressure pain threshold and improving LSST.
References
- 1. W Ben Kibler, Aaron Sciascia. Current concepts; scapular dyskinesis. Br J Sports Me. (2010) Apr;44(5):300-5.
- 2. Maryam Ziaeifara, Amir Massoud Arabb, Zahra Mosallanezhadb and Mohammad Reza Nourbakhsh. Dry needling versus trigger point compression of the upper trapezius: a randomized clinical trial with two-week and three-month follow-up. Journal of Manual & Manipulative Therapy (2019), VOL. 27, NO. 3, 152–161
- 3. Zeinab Ahmadpour Farshad Okhovatian, Marzieh Mohammadi Kojidi, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Hadi Azimi. Comparison of the effects of instrument assisted soft tissue mobilization and dry needling on active myofascial trigger points of upper trapezius muscle. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2021(8 May);35.59.
- 4. Scott W. Cheatham, PT, PhD, DPT, OCS, ATC, CSCS1 Matt Lee, PT, MPT, CSCS2 Matt Cain, MS, CSCS, USAW-I3 Russell Baker, DAT ATC. The efficacy of instrument assisted soft tissue mobilization: a systematic review. (JCCA. 2016; 60(3):200-211)
- 5. C J Odom et al, Measurement of scapular asymetry and assessment of shoulder dysfunction using the Lateral Scapular Slide Test: a reliability and validity study. 2001 Feb; 81(2):799-809
- 6. Nihan Ozunlu et al, Lateral Scapular Slide Test and Scapular Mobility in Volleyball Players J Athl Train.2011 Jul-Aug; 46(4): 438–444.
- 7. ZelihaBaşkurt at al, The effectiveness of scapular stabilization exercise in the patients with subacromial impingement syndrome Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2011;24(3):173-9.
- 8. Dawn T Gulick et al, 2014 Influence of instrument assisted soft tissue treatment techniques on myofascial trigger points. 2014 Oct; 18(4):602
- 9. M Priyanka et al, Compare the Effectiveness of Dry Needling Therapy Versus Cryotherapy on Patients with Upper Trapezius Trigger. Indian Journal of Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy. July-September 2017, 11( 3); 190-193
- 10. Haytham M El-Hafez et al, 2020. Instrument assisted soft tissue obilization versus stripping massage for upper trapezius myofascial triggers points. 2020 Mar6;15(2):87-93.
- 11. Zeinab Ahmadpour Emshi, Farshad Okhovatian,,* Marzieh Mohammadi Kojidi, 1 Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, and Hadi Azimi. Comparison of the effects of instrument assisted soft tissue mobilization and dry needling on active myofascial trigger points of upper trapezius muscle. Med j ishlam repub iran. 2020
- 12. Chen JT, Chung KC, Hou CR, Kuan CR, Chen SM, Hong CZ: Inhibitory Effect of Dry Needling on the Spontaneous Electrical Activity Recorded From Myofascial Trigger Spots of Rabbit Skeletal Muscle. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2000;80:729–735.
- 13. HYUK GA, M.D et al, Dry Needling of Trigger Points with and Without Paraspinal Needling in Myofascial Pain Syndromes in Elderly Patients. The journal of alternative and complementary medicine Volume 13, Number 6, 2007, pp. 617–623
- 14. Jennalyn Lew et al, Comparison of Dry Needling and Trigger Point Manual Therapy in Patients with Neck and Upper Back Myofascial Pain Syndrome: a systematic review and meta analysis. Journal of Manual & Manipulative Therapy 2021, Vol. 29, No. 3, 136–146
- 15. Fahimeh Kamali et al, Comparison of Upper Trapezius and Infraspinatus Myofascial Trigger Point Therapy by Dry Needling in Overhead Athletes with Unilateral Shoulder Impingement Syndrome. Journal of Sport Rehabilitation December 28, 2017
- 16. Juan Rodríguez-Mansilla et al, Effectiveness of dry needling on reducing pain intensity in patients with myofascial pain syndrome: a Meta-analysis. J Tradit Chin Med 2016 February 15; 36(1): 1-13 info@journaltcm.com ISSN 0255 2922
Data Sharing Statement
Funding
Author Contributions
Ethics Declaration
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
About this article
Cite this article
Patel AS, Soni KA. To compare the effectiveness of the dry needling versus instrumented assisted soft tissue mobilization technique on scapular dyskinesia in college students with trapezitis – a comparative study. Physiother Occup Ther J. 2023;16(1):37-49.
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.
| Received | Accepted | Published |
|---|---|---|
| November 12, 2022 | December 22, 2022 | March 29, 2023 |
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21088/potj.0974.5777.16123.3
Keywords
DN; IASTM; Scapular Dyskinesia; Trapezitis; College students.DNIASTMScapular DyskinesiaTrapezitisCollege studentsDN; IASTM; Scapular Dyskinesia; Trapezitis; College students.Search for Similar Articles
Similar Articles
- Exploring the Connection Between Stress, Anxiety, and Central Pain Mechanisms
- Comparative Effectiveness of Mulligan SNAGs and the McKenzie Method in the Mana...
- To Compare the Effectiveness of Dual Task Training Versus Task Oriented Circuit...
- Role of Virtual Reality in Physiotherapy
- Normative Values of One Leg Stance in Urban Adults of 20-40 Years
Article Level Metrics
Last UpdatedSaturday 07 February 2026, 16:11:48 (IST)
Accesses
Citations
Download citation
Article Keywords
Keyword Highlighting
Highlight selected keywords in the article text.
Timeline
| Received | November 12, 2022 |
| Accepted | December 22, 2022 |
| Published | March 29, 2023 |
licence
This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.