Case Report
Role of Topical Heparin in Burn Wound
Ravi Kumar Chittoria, Swathi P, Bharath Prakash Reddy
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.
RFP Journal of Biochemistry and Biophysics 8(1):p 23-26, january-june 2023. | DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21088/rfpjbb.2582-3558.8123.3
How Cite This Article:
Swathi P, Chittoria RK, Reddy BP. Role of topical heparin in burn wound. RFP J Bio Biophy. 2023;8(1):23-6Timeline
Abstract
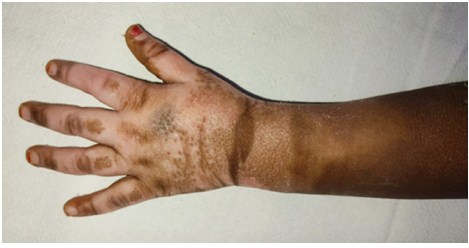
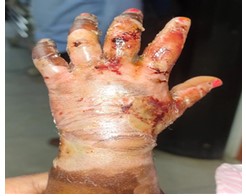
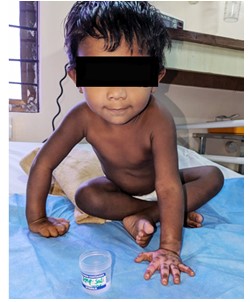
Burns can severely damage a patient's physical and mental health. We should consider pain, hospital stays, lost workdays, and financial strain while handling these patients. Burn patients need rapid specialist care to reduce morbidity and death. Heparin is anti-inflammatory, allergic, histaminic, serotonin blocking, and proteolytic enzyme-blocking. Topical forms have been used to prevent burn extension, limit skin tissue loss, promote quicker healing with fewer contractures, relieve pain, reduce tissue oedema and weeping, prevent infection, and promote revascularization, granulation, and epithelialization of deeply burned tissue. We discuss topical heparin and burn care in this review.
References
- 1. Teot L, Otman S, Brancati A, Mittermayr R. Burn scar treatment. In: Kamolz LP, Jescheke MG, Horch RE, Küntscher M, Brychta P, editors. Handbook of Burns. Vienna: Springer; 2012. p. 55 67.
- 2. Masoud M, Wani AH, Darzi MA. Topical heparin versus conventional treatment in acute burns: a comparative study. Indian J Burns 2014;22:43 50.
- 3. Alrich EM. The effect of heparin on the circulating blood plasma and proteins in experimental burns. Surgery 1949;25:676 80.
- 4. Lu J, Xu T, Yang M, Xu XW, Wu B. Heparin for the treatment of burns (Protocol). Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2011;12:CD009483.
- 5. Reyes A, Astiazaran JA, Chavez CC, Jaramillo F, Saliba MJ. Burns treated with and without heparin: controlled use in a thermal disaster. Ann Burns Fire Disasters 2001;14:183 91.
- 6. Saliba MJ Jr, editor. The Effects of Heparin in the Treatment of Burns. Proceedings of International Meeting; 1994 Feb 24 27.
- 7. Church D, Elsayed S, Reid O, Winston B, Lindsay R. Burn wound infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 2006;19:403 34.
- 8. Saliba MJ Jr, Dempsey WC, Kruggel JL. Large burns in humans. Treatment with heparin. JAMA 1973;225:261 9.
- 9. Ferreira Chacon JM, Mello de Andrea ML, Blanes L, Ferreira LM. Effects of topical application of 10,000 IU heparin on patients with perineal dermatitis and second degree burns treated in a public pediatric hospital. J Tissue Viability 2010;19:150 8.
- 10. Elsayed E, Becker RC. The impact of heparin compounds on cellular inflammatory responses: a construct for future investigation and pharmaceutical development. J Thromb Thrombolysis 2003;15:11 8.
- 11. Saliba M.J. Heparin in the treatment of burns: A review.Burns. 2001;27:348-357.
- 12. Rayes A., Astiazaran J.A., Chavez C.C., Jaramilla F., Saliba M,J. Burns treated with and without heparin: Controlled use in a thermal disaster. Annals of Burnsand Fire Diasters. 2001;14:183-191.
Data Sharing Statement
Funding
Author Contributions
Ethics Declaration
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
About this article
Cite this article
Swathi P, Chittoria RK, Reddy BP. Role of topical heparin in burn wound. RFP J Bio Biophy. 2023;8(1):23-6
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.
| Received | Accepted | Published |
|---|---|---|
| May 24, 2023 | June 09, 2023 | June 30, 2023 |
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21088/rfpjbb.2582-3558.8123.3
Keywords
Topical HeparinWoundManagementBurnSearch for Similar Articles
Similar Articles
- Pharmacological and Phytochemical Insights into Strobilanthes alternata: A Multi...
- The Unseen Pillars: The Foundational Role of Biophysics and Biochemistry in Mode...
- Screen time and its Biochemical Effect on Human beings
- Endocrine Disruption by Heavy Metals: An In-Depth Analytical Review
- How Alloying Affects the Critical Temperature of Low-Temperature Superconductors...
Article Level Metrics
Last UpdatedMonday 26 January 2026, 20:20:39 (IST)
Accesses
Citations
Download citation
Article Keywords
Keyword Highlighting
Highlight selected keywords in the article text.
Timeline
| Received | May 24, 2023 |
| Accepted | June 09, 2023 |
| Published | June 30, 2023 |
licence
This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.