Review Article
Knowledge among Primigravida Mothers Regarding Breastfeeding: A Descriptive Analytical Study
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.
Indian Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 13(4):p 157-165, October-December 2025. | DOI: 10.21088/ijog.2321.1636.13425.4
How Cite This Article:
Kumar D. Knowledge among Primigravida Mothers Regarding Breastfeeding: A Descriptive Analytical Study. Indian J Obstet Gynecol. 2025;13(4):157-165.Timeline
Abstract
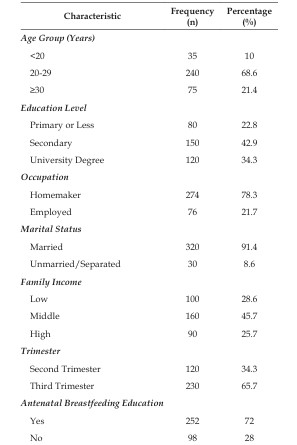
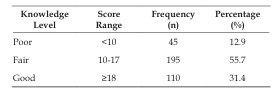
Breastfeeding is globally recognized as a cornerstone of infant and maternal health, offering myriad benefits from reduced infant mortality and morbidity to improved maternal postpartum recovery. However, suboptimal breastfeeding practices remain a significant public health challenge worldwide. Primigravida mothers, experiencing pregnancy and impending motherhood for the first time, represent a particularly vulnerable group whose knowledge and attitudes towards breastfeeding can profoundly influence their initiation and continuation rates. This analytical study aimed to assess the level of knowledge regarding breastfeeding among primigravida mothers attending antenatal clinics and to identify potential gaps and associated factors. A descriptive cross-sectional design was employed, involving a hypothetical sample of 350 primigravida mothers recruited through convenience sampling from selected antenatal clinics in a metropolitan area. A structured questionnaire, encompassing socio-demographic data and 25 knowledge-based questions on benefits, techniques, duration, common problems, and storage, was used for data collection. Data analysis included descriptive statistics (frequencies, percentages, means) and inferential statistics (Chi-square test) to explore associations. Hypothetical results indicate that while primigravidae possessed a moderate overall knowledge level, significant deficiencies were noted regarding specific aspects such as proper latching techniques, management of common breastfeeding problems, and breast milk storage guidelines. Education level and exposure to antenatal breastfeeding education were found to be significantly associated with higher knowledge scores (p<0.05). These findings underscore the critical need for targeted and comprehensive antenatal breastfeeding education programs tailored to the specific knowledge gaps identified among primigravida mothers. Such interventions can empower first-time mothers with the confidence and skills necessary to initiate and sustain optimal breastfeeding practices, ultimately contributing to improved maternal and child health outcomes.
References
- 1. Al-Kohja, K., Al-Shaikh, G. K., Al-Saif, N., Aldosari, N., Mahdi, M., & Al-Khouri, J. (2017). Knowledge, attitude, and practice of breastfeeding among pregnant women in Dubai. International Journal of Women's Health, 9, 747–753.
- 2. Asmare, B., Gebeyehu, E., Boke, M. M., & Tebeje, N. B. (2021). Knowledge, attitude, and associated factors on exclusive breastfeeding among mothers in Debre Tabor Town, Northwest Ethiopia. Journal of Pregnancy, 2021, 5530668.
- 3. Cadwell, K., et al. (2019). Latching and suckling: Assessment and interventions. Journal of Human Lactation, 35(3), 441-454.
- 4. Chowdhury, R., Sinha, B., Sankar, M. J., Taneja, S., Bhandari, N., Rollins, N., Bahl, R., & Martines, J. C. (2015). Breastfeeding and maternal health outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. EBioMedicine, 2(10), 1430 1441.
- 5. IBM Corp. (2019). IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 26.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.
- 6. Kamal, M. F., & Hassan, E. H. (2017). Knowledge and attitude of pregnant women towards breastfeeding in Alexandria, Egypt. Journal of Nursing and Health Science, 6(3), 19-27
- 7. Karlström, A., Tufvegren, E., & Hildingsson, I. (2018). Experiences of breastfeeding and support: a qualitative study of primiparous women in Sweden. International Breastfeeding Journal, 13(1), 16.
- 8. Lim, S. H., Park, S., & Kim, Y. (2019). Factors influencing exclusive breastfeeding rates among Korean mothers: A longitudinal study. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 28(23-24), 4330 4339.
- 9. Rollins, N. C., Bhandari, N., Hajeebhoy, N., Horton, S., Lutter, C. K., Pintag, R., Rasanathan, G. K., & Victora, C. G. (2016). Why invest, and what it will take to improve breastfeeding practices? The Lancet, 387(10017), 491-504.
- 10. UNICEF. (2022). Breastfeeding: A smart investment for healthy women, thriving children and a sustainable future. UNICEF.
- 11. Victora, C. G., Bahl, R., Barros, A. J. D., França, G. V. A., Horton, S., Krasevec, J., Murch, C., ... & Rollins, N. C. (2016). Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong impact. The Lancet, 387(10017), 475 490.
- 12. World Health Organization. (2021). Guidance on counselling pregnant women and mothers of infants and young children on infant and young child feeding. WHO.
- 13. World Health Organization & UNICEF. (2017). Global strategy for infant and young child feeding. WHO.
- 14. World Health Organization. (2022). Breastfeeding and storage of breast milk. WHO. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/ news-room/fact-sheets/detail/infant-and young-child-feeding (Note: Specific link for storage guideline often found within broader IYCF guidance or factsheets).
Data Sharing Statement
Funding
Author Contributions
Ethics Declaration
Acknowledgements
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar D. Knowledge among Primigravida Mothers Regarding Breastfeeding: A Descriptive Analytical Study. Indian J Obstet Gynecol. 2025;13(4):157-165.
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.
| Received | Accepted | Published |
|---|---|---|
| January 02, 2025 | November 29, 2025 | December 24, 2025 |
DOI: 10.21088/ijog.2321.1636.13425.4
Keywords
BreastfeedingPrimigravidaKnowledgeAntenatal CareMaternal and Child HealthInfant NutritionSearch for Similar Articles
Similar Articles
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: Know the Unbeknown
- Healthy Aging and Menopause: Strategies for Indian Women
- Association Between Abnormal Uterine Bleeding and Thyroid Dysfunction: A Cross-S...
- Subsequent Pregnancy After Stillbirth: Risks, Outcomes and Clinical Insights
- Ovarian Carcinoma with Two Discrete Histologies: The Rarest of Rare
Article Level Metrics
Last UpdatedSaturday 28 February 2026, 16:42:20 (IST)
Accesses
Citations
Download citation
Article Keywords
Keyword Highlighting
Highlight selected keywords in the article text.
Timeline
| Received | January 02, 2025 |
| Accepted | November 29, 2025 |
| Published | December 24, 2025 |
licence
This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.