Original Article
Acceptance of Hospital Information Management to Improve the Quality of Healthcare in a Teaching Dental Hospital of Visakhapatnam City: A Mixed-Method Study
RVSSK Kinneresh, L Vamsi Krishna Reddy2, P Swathi, B Suma Priyanka, K Rashmika, Ranjitha Veeramachaneni
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator
RFP Journal of Hospital Administration 8(1):p 19-28, January-June 2024. | DOI: n.a
How Cite This Article:
Kinneresh RVSSK, Reddy LVK, Swathi P, et al. Acceptance of hospital information management to improve the quality of healthcare in a teaching dental hospital of Visakhapatnam city: a mixed-method study. RFP J Hosp Adm. 2024;8(1):19-28.Timeline
Abstract
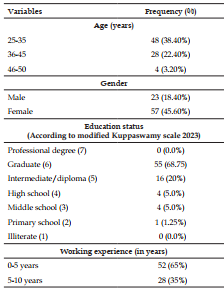
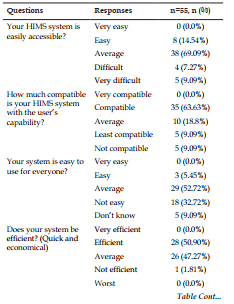
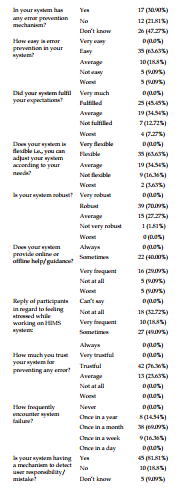
Abstract A health information management system (HIMS) has a set of components (technical, organizational, behavioral) and procedures “organized to generate information to improve health management decisions at all levels of the health system” and also for decision-making process in hospital. Engaging clinicians and other hospital personnel, including nurses, as wellas providing strong institutional support, is critical to the successful implementation and operation of a HIMS in hospitals. Aim: To assess the acceptance of a hospital information system to improve healthcare quality in a teaching hospital of Visakhapatnam city. Methodology: An Institution-based mixed-method study both quantitative and qualitative data collection methods was conducted at Teaching Hospital of Visakhapatnam city for duration of 3 months. A total sample of 80 health care workers (HCWs) working in Teaching Hospital, who were managing administrative hospital staff, heading sub-process, departments, and nurses were enrolled in the present study. Results: Most (38.40%) of our participants belonged to the age group of 25–35 years. The majority (45.60%) of them were females. The majority (69.70%) of them had bachelor’s degrees and 65% had work experience from 0-5 years.
References
- 1. Ismail, A., Jamil, A. T., Fareed, A., Rahman, A., Madihah, J., Bakar, A. & Saadi, H. (2012). The implementation of Hospital Information System (HIS) in tertiary hospitals in Malaysia: a qualitative study.
- 2. Shortliffe, E. H., & Barnett, G. O. (2014). Biomedical data: Their acquisition, storage, and use. In Biomedical informatics (pp. 39-66). Springer London.
- 3. Buntin, M. B., Burke, M. F., Hoaglin, M. C., & Blumenthal, D. (2011). The benefits of health information technology: a review of the recent literature shows predominantly positive results. Health affairs, 30(3), 464-471.
- 4. Ketikidis, P., Dimitrovski, T., Lazuras, L., & Bath, P. A. (2012). Acceptance of health information technology in health professionals: an application of the revised technology acceptance model. Health informatics journal, 18(2), 124-134.
- 5. Prakash B. Patient satisfaction and normative decision theory. J Cutan Aesthet Surg 2010; 3:280.
- 6. Read “The Future of the Public’s Health in the 21st Century” at NAP.edu [Internet]. [Accessed on Mar 24, 2023]. Available from: https:// www.nap.edu/ read/10548/chapter/1
- 7. Mahla M, Talati S, Gupta AK, Agarwal R, Tripathi S, Bhattacharya S. The acceptance level of Hospital Information Management System (HIMS) among the nursing officials working in a teaching hospital. J Edu Health Promot 2021; 10:452.
- 8. Ebnehoseini Z, Tabesh H, Deldar K, Mostafavi SM, Tara M. Determining the Hospital Information System (HIS) Success Rate: Development of A New Instrument and Case Study. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019 May 15; 7(9):1407-1414.
- 9. Sanjuluca, T.H.P.; de Almeida, A.A.; Cruz-Correia, R. Assessing the Use of Hospital Information Systems (HIS) to Support Decision-Making: A Cross-Sectional Study in Public Hospitals in the Huíla Health Region of Southern Angola. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1267.
- 10. Khalifa M, Alswailem O. Hospital information systems (HIS) acceptance and satisfaction: A case study of a Tertiary Care Hospital. In: Procedia Computer Science. London, U.K. Elsevier B.V; 2015. p. 198-204.
- 11. Alipour J, Zarei A. Health information technology acceptance factors by caregivers in nursing home facilities in Iran Health information technology acceptance factors by caregivers in nursing home facilities in Iran. Bir J Med Sci 2017; 16:506-12.
- 12. Huryk LA. Factors influencing nurses’ attitudes towards healthcare information technology. J Nurs Manag 2010; 18:606-12.
- 13. Ducey AJ, Coovert MD. Predicting tablet computer use: An extended Technology Acceptance Model for physicians. Health Policy Tech 2016; 5:268-84.
- 14. Chen RF, Hsiao JL. An empirical study of physicians’ acceptance of hospital information systems in Taiwan. Telemed J E Health 2012;18(2):120-5.
- 15. Wangenheim A, de Souza Nobre LF, Tognoli H, et al. User Satisfaction with Asynchronous Telemedicine: A Study of Users of Santa Catarina’s System of Telemedicine and Telehealth. Telemed J E Health 2012;18(5):339-46.
- 16. Bhattacharya S, Kumar A, Kaushal V, Singh A. Applications of m-Health and e- Health in Public Health sector: The Challenges and Opportunities. Int J Med Public Health. 2018;8(2):56-7.
- 17. Moradipour M, Javidi M, Sadeghi T. Effects of Hospital Information System on the Performance of Management Units in Public Hospitals Analysis in Southwestern Iran. Jundishapur J Health Sci. 2022;14(1): e119762.
- 18. Sanjuluca THP, de Almeida AA, Cruz-Correia R. Assessing the Use of Hospital Information Systems (HIS) to Support Decision-Making: A CrossSectional Study in Public Hospitals in the Huíla Health Region of Southern Angola. Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Jul 7;10(7):1267.
- 19. Ebnehoseini, Zahra & Tabesh, Hamed & Deldar, Kolsoum & Mostafavi, Seyed & Tara, Mahmood. Determining Hospital Information System (HIS) Success Rate: Development of a New Instrument and Case Study. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences. 7. 1407-1414. 10.3889/ oamjms.2019.294.
- 20. Khalifa, Mohamed & Alswailem, Osama. Hospital Information Systems (HIS) Acceptance and Satisfaction: A Case Study of a Tertiary Care Hospital. Procedia Computer Science. 63. 198-204. 10.1016/j.procs.2015.08.334.
- 21. Hidayanto, Achmad. Information Technology Assessment on Hospital Information System Implementation: Case Study A Teaching Hospital. International Journal of Engineering and Technology. 5. 631-634.
- 22. Sakineh Saghaeiannejad-Isfahani, Marya Jahanbakhsh, Mahboobeh Habibi Razieh Mirzaeian, Mansoreh Nasirian, and Javad Sharifi Rad. A Survey on the Users’ Satisfaction with the Hospital Information Systems (HISs) based on DeLone and McLean’s Model in the Medical-Teaching Hospitals in Isfahan City, Acta Inform Med. 2014 Jun; 22(3): 179–182.
- 23. Javak Derakhshani, Majid Vahedi. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Hospital Information System [HIS] (Case study: Tabriz Teaching Hospitals) Depiction of Health. 2015;6(2): 1-7.
- 24. Vafaee, A., Vahedian, M., Esmaeily, H., Kimiafar, K. Views of Users towards the Quality of Hospital Information System in Training Hospitals. Journal of Research in Health Sciences, North America, 10, Jun. 2010.
- 25. Cruz-Correia R, Boldt I, Lapão L, et al. Analysis of the quality of hospital information systems audit trails. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 2013;13(1):84.
- 26. Moghadam, Mohammad & Fayaz-Bakhsh, Ahmad. Hospital information system utilization in Iran: A qualitative study. Acta medica Iranica. 52. 855-9.
- 27. Pandit AP, Debmallik T, Kulkarni M. A Study on the Utilization of Hospital Information System (Ward and Physician) Modules in a Tertiary Care Hospital.
Data Sharing Statement
Funding
Author Contributions
Ethics Declaration
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
About this article
Cite this article
Kinneresh RVSSK, Reddy LVK, Swathi P, et al. Acceptance of hospital information management to improve the quality of healthcare in a teaching dental hospital of Visakhapatnam city: a mixed-method study. RFP J Hosp Adm. 2024;8(1):19-28.
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator
| Received | Accepted | Published |
|---|---|---|
| March 28, 2024 | May 08, 2024 | June 30, 2024 |
DOI: n.a
Keywords
Hospital Information ManagementHIMSMixed-methodQuality of HealthcareAcceptanceSearch for Similar Articles
Similar Articles
- Role of Fibrinogen Concentrate and Its Effect on Blood Loss in on Pump Cardiac S...
- From Sequencing to Prediction: Leveraging Next Generation Sequencing & Machine L...
- The Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023: Forensic and Medicolegal Implica...
- Perception of “Young Adults” on Integration of Telemedicine in Healthcare Servic...
- Accomplishment of International Patient Safety Goals (IPSG) in Enhancing Patient...
Article Level Metrics
Last UpdatedMonday 26 January 2026, 19:18:44 (IST)
Accesses
Citations
Download citation
Article Keywords
Keyword Highlighting
Highlight selected keywords in the article text.
Timeline
| Received | March 28, 2024 |
| Accepted | May 08, 2024 |
| Published | June 30, 2024 |
licence
This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator