Review Article
A Comprehensive Review of Autonomic Function Testing
Mona Bedi, , Pooja Nigade1 , V.P. Varshney2 , Mona Bedi3
Licence:
International Physiology 12(2-3):p 43-49, May -Dec. 2024. | DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.21088/ip.2347.1506.122234.1
How Cite This Article:
Pooja Nigade, V.P. Varshney, Mona Bedi. A Comprehensive Review of Autonomic Function Testing. Int. Phy.2024;12(2-3):43–49.
Timeline
Abstract
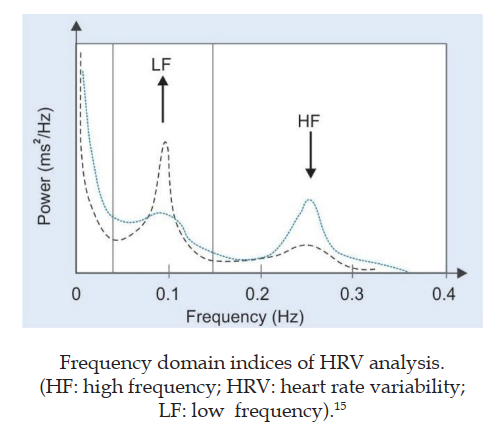
The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates numerous involuntary bodily functions, including cardiovascular control, digestion, and thermoregulation. Disruptions in ANS function are associated with a diverse array of neurological and systemic disorders. Traditional autonomic testing methods, such as the Valsalva manoeuvre and orthostatic tests, primarily focus on cardiovascular reflexes, offering valuable yet indirect insights into autonomic pathways. However, technological advancements have led to the emergence of modern methods like heart rate variability (HRV) analysis, microneurography, and quantitative sudomotor axon reflex testing (QSART), which provide more precise assessments of both sympathetic and parasympathetic function. Despite their potential, the integration of these contemporary methods into routine clinical practice remains limited due to their complexity and resource requirements. This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of classical and modern ANS testing methods, emphasising their clinical relevance in daily practice to enhance patient-care. Aims and Methods of ANS Testing: Autonomic nervous system (ANS) testing is essential for evaluating the severity and distribution of autonomic dysfunction, diagnosing conditions such as autonomic neuropathy and orthostatic intolerance, and monitoring disease progression or treatment efficacy. Most tests assess cardiovascular reflexes in response to various stimuli, activating sympathetic or parasympathetic outflow. Classical methods, including the Ewing Battery, Head-Up Tilt (HUT) test, and Deep Breathing Test, remain clinically significant, especially in settings lacking advanced technology. Contemporary methods have revolutionised ANS testing, with HRV analysis providing in-depth insights into autonomic control over heart rate, while Microneurography and QSART assess sympathetic nerve activity and sudomotor function, respectively. Conclusion: The evolution of autonomic function testing, from simple measures to advanced techniques, enhances our understanding of ANS regulation. Classical methods remain invaluable, yet newer technologies like HRV analysis and QSART offer detailed evaluations for complex autonomic conditions. Broad clinical integration of these contemporary methods alongside traditional approaches is essential for improving patient care.
References
No records found.
About this article
Cite this article
Pooja Nigade, V.P. Varshney, Mona Bedi. A Comprehensive Review of Autonomic Function Testing. Int. Phy.2024;12(2-3):43–49.
Licence:
| Received | Accepted | Published |
|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | N/A |
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.21088/ip.2347.1506.122234.1
Keywords
ANS testingANSNewer methods of ANS testing.Search for Similar Articles
Similar Articles
Article Level Metrics
Last UpdatedSaturday 07 February 2026, 21:59:25 (IST)
Accesses
Citations
Download citation
Article Keywords
Keyword Highlighting
Highlight selected keywords in the article text.
Timeline
| Received | N/A |
| Accepted | N/A |
| Published | N/A |