Case Report
Sheer Sinisterness of Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus: Parapharyngeal Abscess
Redkar Aditya Achyut, Apoorva P, Rajesh Radhakrishna Havaldar, Shilpa Mallapur, Neema K
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator
RFP Journal of ENT and Allied Sciences 8(1):p 15-19, January-June 2023. | DOI: NA
How Cite This Article:
Apoorva P, Havaldar RR, Mallapur S, et al. Sheer sinisterness of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus: Parapharyngeal abscess. RFP J ENT Allied Sci. 2023;8(1):15–19.Timeline
Abstract
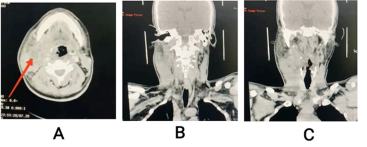
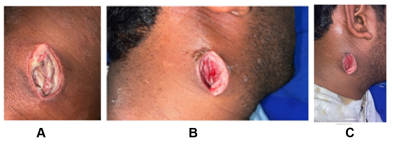
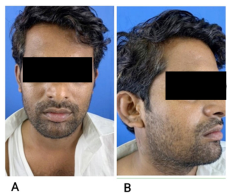
Diabetes mellitus is a common disease in developing countries and the complications are feared by many physicians and surgeons. One such rare and dangerous complication is parapharygeal abscess which can spread via its intricate anatomical site to other deep neck spaces. We present the case of a young male who is a known uncontrolled diabetic presented to us with neck swelling and toxic symptoms and managed successfully with timely surgical intervention by exploring all neck planes to evacuate purulent material thus speeding up the recovery process.
References
- 1. Guo, Bei-CyuanMDa,b; Wu, Han-Ping MD, PhDa,b,c,*. Deep neck infections with mediastinum abscess and respiratory failure in a pediatric patient: A case report. Medicine Case Reports and Study Protocols 2(7):p e0122, July 2021. | DOI: 10.1097/ MD9.000000000000012.
- 2. Pentapati, Siva Santosh Kumar; Debnath, DhrubajyotiJ.. Updated BG Prasad’s classification for the year 2022. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care 12(1):p 189-190, January 2023. | DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1478_22.
- 3. Hasegawa J, Hidaka H, Tateda M, Kudo T, Sagai S, Miyazaki M, Katagiri K, Nakanome A, Ishida E, Ozawa D, Kobayashi T. An analysis of clinical risk factors of deep neck infection. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2011 Feb; 38(1):101-7. Doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2010.06.001. Epub 2010 Jul 6. PMID: 20609540.
- 4. Caccamese Jr JF, Coletti DP. Deep neck infections: clinical considerations in aggressive disease. Oral MaxillofacSurg Clin North Am 2008; 20:367–80. Doi: 10.1016/j.coms.2008.03.001.
- 5. Marioni G, Staffieri A, Parisi S, et al. Rational diagnostic and therapeutic management of deep neck infections: analysis of 233 consecutive cases. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2010;119(3):181-187. Doi: 10.1177/000348941011900306.
- 6. Meher R, Jain A, Sabharwal A, Gupta B, Singh I, Agarwal AK. Deep neck abscess: a prospective study of 54 cases. J Laryngol Otol. 2005;119(4):299-302. Doi: 10.1258/0022215054020395.
- 7. Huang TT, Liu TC, Chen PR, Tseng FY, Yeh TH, Chen YS. Deep neck infection: analysis of 185 cases. Head Neck. 2004;26:854-860.
- 8. Lalakea ML, Messner AH. Retropharyngeal abscess management in children: current practices. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1999;121: 398 - 405.
- 9. Bakir S, Tanriverdi MH, Gun R, et al. Deep neck space infections: a retrospective review of 173 cases. Am J Otolaryngol. 2012;33(1):56-63. Doi: 10.1016/j. amjoto.2011.01.003.
- 10. Vieira F, Allen SM, Stocks RSM, et al. Deep neck infections. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 2008;12:459–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2008.01.002.
- 11. Parhiscar A, Har-El G (2001) Deep neck abscess: a retrospective review of 210 cases. Ann OtolRhinolLaryngol 110(11):1051– 1054.
- 12. Eftekharian A, Roozbahany NA, Vaezeafshar R, Narimani N. Deep neck infections: a retrospective review of 112 cases. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;266(2):273-277. Doi: 10.1007/s00405-008-0734-5
Data Sharing Statement
Funding
Author Contributions
Ethics Declaration
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
About this article
Cite this article
Apoorva P, Havaldar RR, Mallapur S, et al. Sheer sinisterness of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus: Parapharyngeal abscess. RFP J ENT Allied Sci. 2023;8(1):15–19.
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator
| Received | Accepted | Published |
|---|---|---|
| May 25, 2023 | June 22, 2023 | June 30, 2023 |
DOI: NA
Keywords
Parapharyngeal space; Diabetes Mellitus; Klebsiella; Abscess; DNSI.Parapharyngeal spaceDiabetes MellitusKlebsiellaAbscessDNSISearch for Similar Articles
Similar Articles
- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in an Immunocompetent Individual with Acute Tonsillitis;...
- Hidden Dangers of Oral Hygiene: Oropharyngeal Impalement by Toothbrush in a 3-Ye...
- Functional Outcome of Abbe–Estlander Flap in Lower Lip Carcinoma with Commissura...
- Primary Laryngeal Histoplasmosis
- Inverted Papilloma a Retrospective Study of 17 Cases
Article Level Metrics
Last UpdatedMonday 26 January 2026, 20:22:43 (IST)
Accesses
Citations
Download citation
Article Keywords
Keyword Highlighting
Highlight selected keywords in the article text.
Timeline
| Received | May 25, 2023 |
| Accepted | June 22, 2023 |
| Published | June 30, 2023 |
licence
This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator