Case Report
Surgical Prognostic Factors for Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma
Keshav Gupta, Deepa Kumari, Shreya Jain, Prag Kumari
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator
RFP Journal of ENT and Allied Sciences 9(1):p 71-75, January-June 2024. | DOI: NA
How Cite This Article:
Gupta K, Kumari D, et al. Surgical prognostic factors for juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. RFP J ENT Allied Sci. 2024;9(1):71–75.Timeline
Abstract
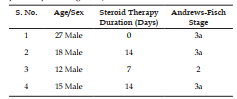
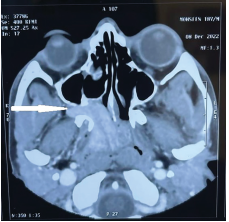
Background: Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma (JNA) are benign, rare and highly vascular tumors of nose and para nasal sinuses seen only in post pubertal males. Aim: To study surgical prognostic factors for JNA. Objectives: To study the effect of presenting features namely blood supply, blood loss, tumor grading, steroid therapy and age of presentation on surgical prognosis. Material: Presenting features and surgical outcomes of all 4 operated JNA patients were compared from the Departmental records. Result: Unilateral blood supply, Lesser pre-operative blood loss, lesser grade tumor, longer steroid therapy and more age at presentation have better surgical outcome. Conclusion: Although benign and rare to encounter, their diagnosis and management is a challenge owing to their highly vascular nature and their blood supply directly from or from main branches of carotid arteries. Here, we present four cases of successful management of JNA with detailed discussion of surgical prognostic factors of the rare tumor
References
- 1. Tork C.A., Simpson D.L. Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma. [Updated 2022 Jun 27]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/ NBK545240/
- 2. Safadi A., Schreiber A., Fliss D.M., Nicolai P. Juvenile Angiofibroma: Current Management Strategies. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2018 Feb; 79(1):21-30. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1615810. Epub 2018 Jan. 18. PMID: 29404237; PMCID: PMC5796815.
- 3. Butler C.R., Scholfield D.W., Madani G., Sandison A., Clarke P.M. Current Management and Controversies of Juvenile Angiofibromas. Int J. Head Neck Surg 2018; 9(1):32-37.
- 4. Makhasana J.A., Kulkarni MA, Vaze S, Shroff AS. Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2016 May-Aug;20(2):330.
- 5. Alshaikh N.A., Eleftheriadou A. Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma staging: An overview. Ear Nose Throat J. 2015 Jun; 94(6):E12-22.
- 6. Allensworth J.J., Troob S.H., Lanciault C., Andersen P.E. High-grade malignant transformation of a radiation-naïve nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Head Neck. 2016 Apr; 38 Suppl 1:E2425-7
- 7. Park C.K., Kim D.G., Paek S.H., Chung H.T., Jung H.W. Recurrent juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma treated with gamma knife surgery. J. Korean Med Sci. 2006 Aug; 21(4):773-7.
- 8. Overdevest J.B., Amans M.R., Zaki P., Pletcher S.D., El-Sayed I.H. Patterns of vascularization and surgical morbidity in juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: A case series, systematic review, and meta-analysis. Head Neck. 2018 Feb; 40(2):428-443.
- 9. Wai Lup Wong and Bal Sanghera. Recent advances in technology. In John C Watkinson and Raymond W Clarke. Scott Brown’s Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery. 8th ed. New York: CRC Press;2018.p541-58.
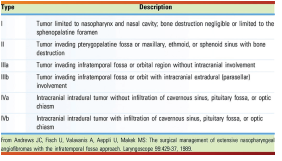
- 10. Andrews J.C., Fisch U., Valavanis A., Aeppli U., Makek M.S. The surgical management of extensive nasopharyngeal angiofibromas with the infratemporal fossa approach. Laryngoscope 1989; 99:429-37.
- 11. James V. Byrne. Interventional Techniques. In John C. Watkinson and Raymond W. Clarke. Scott Brown’s Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery. 8th ed. New York: CRC Press; 2018. p 569-80.
- 12. Mehan R., Rupa V., Lukka V.K., Ahmed M., Moses V., Shyam Kumar N.K. Association between vascular supply, stage and tumour size of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Dec;273(12):4295-4303.
Data Sharing Statement
Funding
Author Contributions
Ethics Declaration
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta K, Kumari D, et al. Surgical prognostic factors for juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. RFP J ENT Allied Sci. 2024;9(1):71–75.
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator
| Received | Accepted | Published |
|---|---|---|
| March 16, 2024 | May 27, 2024 | June 30, 2024 |
DOI: NA
Keywords
Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma JNA vascular tumor surgery prognosis.JuvenilenasopharyngealangiofibromaJNAvasculartumorsurgeryprognosisSearch for Similar Articles
Similar Articles
- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in an Immunocompetent Individual with Acute Tonsillitis;...
- Hidden Dangers of Oral Hygiene: Oropharyngeal Impalement by Toothbrush in a 3-Ye...
- Functional Outcome of Abbe–Estlander Flap in Lower Lip Carcinoma with Commissura...
- Primary Laryngeal Histoplasmosis
- Inverted Papilloma a Retrospective Study of 17 Cases
Article Level Metrics
Last UpdatedMonday 26 January 2026, 20:21:38 (IST)
Accesses
Citations
Download citation
Article Keywords
Keyword Highlighting
Highlight selected keywords in the article text.
Timeline
| Received | March 16, 2024 |
| Accepted | May 27, 2024 |
| Published | June 30, 2024 |
licence
This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator