Original Article
Role of Silver Alginate Dressings on Split Skin Graft Site to Prevent Post-operative Infection
Ravi Kumar Chittoria , Geetankshi Gopal Ghabru1 , Ravi Kumar Chittoria2 , Amrutha J S3
Licence:
RFP Indian Journal of Hospital Infection 6(1):p 7-10, Jan-June 2024. | DOI: n.a
How Cite This Article:
Geetankshi Gopal Ghabru, Ravi Kumar Chittoria, Amrutha J S. Role of Silver Alginate Dressings on Split Skin Graft Site to Prevent Postoperative Infection. RFP Ind. Jr. Hosp. Inf., 2024,6(1):07–10.
Timeline
Abstract
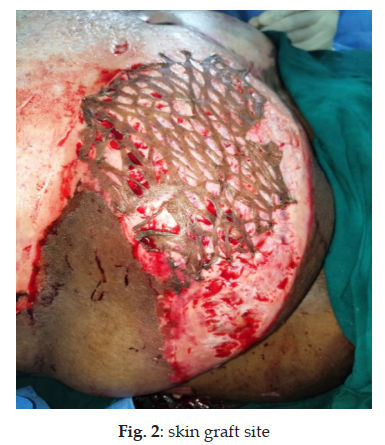
Burn injuries can be devastating, not only causing physical pain and trauma but also increasing the risk of infections, which can further complicate the healing process. Therefore, finding effective methods to prevent postoperative infections is crucial for the successful treatment of burn patients. In this study we consider the effectiveness of silver containing alginate dressings for deep partial thickness burns in a patient with accidental thermal burns. Silver alginate dressings consist of a combination of silver and sodium alginate, a natural polysaccharide derived from seaweed. The silver in it has antimicrobial properties, making it an ideal choice for preventing infection. The dressings are available in various forms, such as sheets, dressings, and ropes, allowing for versatile usage in wound care management. They are able to maintain a moist environment as well as prevents wound infection. They are found to be useful in various conditions including burn wound, skin graft donor site and other conditions like pressure injuries. Silver alginate dressings are highly effective in managing burn wounds due to their unique combination of antimicrobial and wound-healing properties. The alginate interacts with wound exudate to form a gel, maintaining a moist wound environment that promotes tissue regeneration, while the silver provides broadspectrum antimicrobial action, preventing infections caused by bacteria, fungi, and even antibioticresistant pathogens like MRSA. In burn care, silver alginate dressings are particularly beneficial for partial-thickness burns (second-degree burns) and donor sites after skin grafting. They are highly absorbent, making them suitable for burns with moderate to heavy exudate, while reducing the risk of maceration in surrounding skin. The gel formation also minimizes pain during dressing changes, as it prevents adhesion to the wound bed.
References
No records found.
About this article
Cite this article
Geetankshi Gopal Ghabru, Ravi Kumar Chittoria, Amrutha J S. Role of Silver Alginate Dressings on Split Skin Graft Site to Prevent Postoperative Infection. RFP Ind. Jr. Hosp. Inf., 2024,6(1):07–10.
Licence:
| Received | Accepted | Published |
|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | N/A |
DOI: n.a
Keywords
Silver; Alginates; SSG site; Donor site; Post-op infectionSearch for Similar Articles
Similar Articles
- Surgical Site Infections: A Review and the Critical Role of Nurses in Preventio...
- Microbial Degradation of Bioplastics: Mechanisms, Challenges, and Future Prospe...
- Incidence and Grading of Surgical Site Infections Using the Southampton System...
- TP53 as a Tumor Suppressor Gene
- Prevailing Hospital Acquired Infections a Challenge to Safety of Patients and Ho...
Article Level Metrics
Last UpdatedTuesday 27 January 2026, 01:18:08 (IST)
Accesses
Citations
Download citation
Article Keywords
Keyword Highlighting
Highlight selected keywords in the article text.
Timeline
| Received | N/A |
| Accepted | N/A |
| Published | N/A |