Original Article
Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Conventional Curettage Adenoidectomy and Alternative Surgical Techniques
Likhitha V, Mithra Miriam Mathews, Greeshma K
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator
RFP Journal of ENT and Allied Sciences 10(1):p 7-12, Jan-June 2025. | DOI: 10.21088/rjeas.2456.5024.10125.1
How Cite This Article:
Likhitha V, Mathews MM, Greeshma K. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of conventional curettage adenoidectomy and alternative surgical techniques. RFP J ENT Allied Sci. 2025;10(1):7-12.Timeline
Abstract
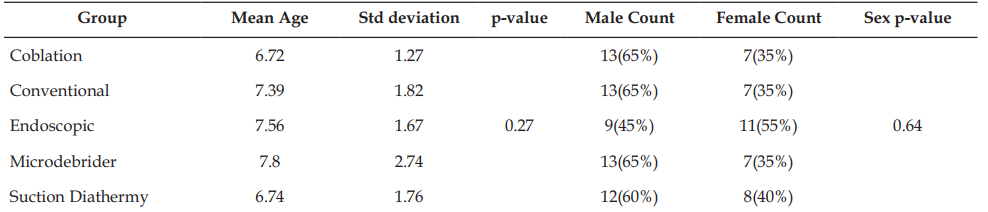
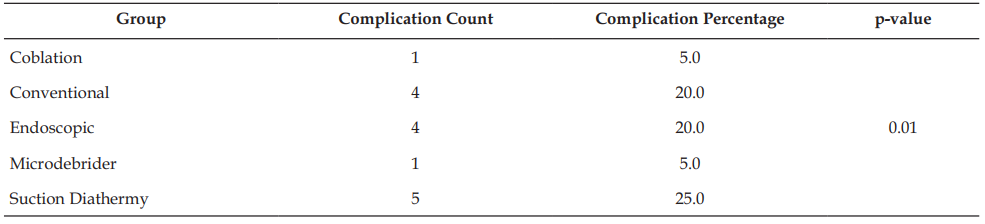
Introduction: Adenoidectomy is a widely performed surgical procedure for managing chronic adenoid hypertrophy, which can contribute to nasal obstruction, recurrent otitis media, and obstructive sleep apnea in children. Conventional curettage adenoidectomy has been the standard technique; however, concerns regarding residual adenoid tissue, intraoperative bleeding, and postoperative morbidity have led to the adoption of newer techniques, including Coblation, Microdebrider-assisted, Suction Diathermy, and Endoscopic-assisted adenoidectomy. This study aims to compare the efficacy and safety of these techniques with conventional curettage adenoidectomy in terms of intraoperative blood loss, operative time, residual adenoid tissue, and postoperative complications. Materials and Methods: This prospective, comparative study included 100 pediatric patients (aged 3–12 years) undergoing adenoidectomy. Patients were randomly assigned to one of five groups: Conventional curettage, Coblation, Microdebrider assisted, Suction Diathermy, and Endoscopic-assisted adenoidectomy. Primary outcomes assessed included operative time, intraoperative blood loss, and completeness of adenoid removal via postoperative endoscopy. Secondary outcomes included postoperative pain scores, time to resume normal diet, and complications such as bleeding and velopharyngeal insufficiency. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS software, with significance set at p <0.05.Results: Coblation demonstrated the shortest operative time (9.7 minutes), significantly lower intraoperative blood loss (20.5 ml), and the least residual adenoid tissue (15%) compared to conventional curettage (20.1 minutes, 50.9 ml blood loss, and 70% residual tissue). Postoperative pain scores were lowest in the Coblation group (3.6), whereas the highest was observed in the conventional curettage group (6.3). The complication rate was lowest in Coblation (5%) compared to Conventional (20%) and Suction Diathermy (25%). Conclusion: Coblation adenoidectomy offers significant advantages over conventional curettage, including reduced operative time, minimal intraoperative blood loss, and lower residual adenoid tissue with fewer complications. These findings suggest that Coblation may be the preferred technique for pediatric adenoidectomy. However, further long-term studies are warranted to validate these findings.
References
- 1. Singh J, Bhardwaj B. The Comparison between Microdebrider Assisted Adenoidectomy and Coblation Adenoidectomy: Analyzing the Intraoperative Parameters and Post-operative Recovery. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Mar;72(1):59-65. doi: 10.1007/ s12070-019-01736-5. Epub 2019 Sep 27. PMID: 32158657; PMCID: PMC7040151.
- 2. Zainea V. Conventional curettage adenoidectomy versus endoscopic assisted adenoidectomy. Maedica (Bucur). 2011 Oct;6(4):328-9. PMID: 22879849; PMCID: PMC3391952.
- 3. Ali, A.A.A.E., Elsharnouby, M.K., Khalil, Y.A.E. et al. Evaluation of endoscopic assisted suction coagulation adenoidectomy versus traditional curettage technique. Egypt J Otolaryngol 37, 122 (2021). https://doi. org/10.1186/s43163-021-00173-y.
- 4. Bidaye R, Vaid N, Desarda K. Comparative analysis of conventional cold curettage versus endoscopic assisted coblation adenoidectomy. The Journal of Laryngology & Otology. 2019;133(4):294-299. doi:10.1017/ S0022215119000227
- 5. Aref ZF, Badawy SB, Abdelraheem AG, Mohamed EA, Tayaa U. A Comparative Study between Coblation Adenoidectomy and Conventional Adenoidectomy. SVU Int J Med Sci. 2022;5(1):155-163.
- 6. El Tahan AR, Elzayat S, Hegazy H. Adenoidectomy: comparison between the conventional curettage technique and the coblation technique in pediatric patients. Egypt J Otolaryngol. 2016;32(3):152.
- 7. Hapalia VB, Panchal AJ, Kumar R, Kapadia PB, Bhiryani MA, Verma RB, Parmar ND. Pediatric Adenoidectomy: A Comparative Study Between Cold Curettage and Coblation Technique. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Oct;74(Suppl 2):1163-1168. doi: 10.1007/s12070-020-02247-4. Epub 2020 Oct 30. PMID: 36452765; PMCID: PMC9702207.
- 8. Calvo-Henriquez, C., RuedaFernandezRueda, M., Garcia-Lliberos, A. et al. Coblator adenoidectomy in pediatric patients: a state-ofthe-art review. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 280, 4339–4349 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/ s00405-023-08094-7
- 9. Somani SS, Naik CS, Bangad SV. Endoscopic adenoidectomy with microdebrider. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 Oct;62(4):427-31. doi: 10.1007/s12070-011- 0118-9. Epub 2011 Jan 11. PMID: 22319707; PMCID: PMC3266095.
- 10. Malas, M., Althobaiti, A.A., Sindi, A. et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of conventional curettage adenoidectomy with those of other adenoidectomy surgical techniques: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J of Otolaryngol - Head & Neck Surg 52, 21 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/ s40463-023-00634-9
- 11. Kim JW, Kim HJ, Lee WH, et al. Comparative study for efficacy and safety of adenoidectomy according to the surgical method: A prospective multicenter study. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0135304. doi: 10.1371/journal. pone.0135304. PMID: 26267337; PMCID: PMC4534417.
- 12. Yang L, Shan Y, Wang S, Cai C, Zhang H. Endoscopic assisted adenoidectomy versus conventional curettage adenoidectomy:a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. SpringerPlus. 2016;5:426.
Data Sharing Statement
Funding
Author Contributions
Ethics Declaration
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
About this article
Cite this article
Likhitha V, Mathews MM, Greeshma K. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of conventional curettage adenoidectomy and alternative surgical techniques. RFP J ENT Allied Sci. 2025;10(1):7-12.
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator
| Received | Accepted | Published |
|---|---|---|
| March 17, 2025 | April 16, 2025 | June 30, 2025 |
DOI: 10.21088/rjeas.2456.5024.10125.1
Keywords
AdenoidectomyEfficacy and SafetySurgical TechniquesSearch for Similar Articles
Similar Articles
- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in an Immunocompetent Individual with Acute Tonsillitis;...
- Hidden Dangers of Oral Hygiene: Oropharyngeal Impalement by Toothbrush in a 3-Ye...
- Functional Outcome of Abbe–Estlander Flap in Lower Lip Carcinoma with Commissura...
- Primary Laryngeal Histoplasmosis
- Inverted Papilloma a Retrospective Study of 17 Cases
Article Level Metrics
Last UpdatedMonday 26 January 2026, 20:23:51 (IST)
Accesses
Citations
Download citation
Article Keywords
Keyword Highlighting
Highlight selected keywords in the article text.
Timeline
| Received | March 17, 2025 |
| Accepted | April 16, 2025 |
| Published | June 30, 2025 |
licence
This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator