Original Article
User Perception of ChatGPT and Traditional Reference Services
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.
Indian Journal of Library and Information Science 19(3):p 209-213, Sep-Dec 2025. | DOI: 10.21088/ijlis.0973.9548.19325.1
How Cite This Article:
Mondal D. User Perception of ChatGPT and Traditional Reference Services. Ind J Lib Inf Sci. 2025;19(3):209-13.Timeline
Abstract
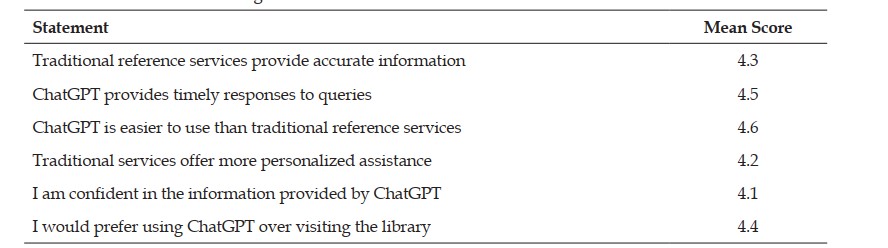
The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has significantly transformed library reference services, particularly through the introduction of conversational agents such as ChatGPT. This study explores user perceptions of ChatGPT in comparison to traditional reference services provided by human librarians. Employing a surveybased methodology, data were collected from academic library users to assess key factors including accuracy, trustworthiness, user satisfaction, response time, and ease of use. The findings indicate that although ChatGPT delivers rapid and easily accessible support, users generally prefer traditional reference services for complex or specialized queries, attributing this preference to the human capacity for contextual understanding and critical thinking. The study underscores the complementary roles of AI and human librarians, proposing that the integration of ChatGPT as a supportive tool can enhance the overall effectiveness of reference service delivery. These insights offer valuable guidance for libraries aiming to innovate while aligning with user expectations in a rapidly evolving information environment.
References
- 1. Choi Y, Hickman SE, Kang H. Exploring ChatGPT’s role in academic libraries: Opportunities and limitations. J Libr Innov. 2023;14(1):22–35.
- 2. Floridi L, Chiriatti M. GPT-3: Its nature, scope, limits, and consequences. Minds Mach. 2020;30(4):681–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/ s11023-020-09548-1.
- 3. Head AJ, Eisenberg MB. AI and the future of information literacy: Understanding student use of ChatGPT. Proj Inf Lit Res Brief. 2022;5(2):1–12.
- 4. Lin S, Yu M. Comparing virtual AI and human reference services: A user experience study. Coll Res Libr. 2022;83(6):987–1003. https:// doi.org/10.5860/crl.83.6.987.
- 5. Radford ML. Communication theory applied to the reference encounter: An analysis of critical incidents. Libr Q. 2006;76(3):317–40. https://doi.org/10.1086/511140.
- 6. Tenopir C. Use and users of electronic library resources: An overview and analysis of recent research studies. Council on Library and Information Resources; 2004. https://www. clir.org/pubs/reports/pub120/.
- 7. Zhang Q, Liu Y. Evaluating ChatGPT in academic information services: Accuracy, reliability, and user trust. Inf Technol Libr. 2023;42(1):55–70.
- 8. Mondal D. Growth and development of National Digital Library of India since inception under the initiative of IIT Kharagpur: A comprehensive study. Libr Philos Pract (e-journal). 2021;6248. https:// digitalcommons.unl.edu/libphilprac/6248.
- 9. Mondal D. The practice of mobile learning in the digital age: A case study for U.G students, Durgapur, W.B, India. Libr Philos Pract (e-journal). 2023;7723. https:// digitalcommons.unl.edu/libphilprac/7723.
- 10. Mondal D. Artificial Intelligence (AI): A transformative force, redefining the landscape of modern libraries. INQEST. 2025;3(1):15–23.
- 11. Mondal D. AI-driven growth: Transforming professional development for LIS educators. 2025. https://hq.ssrn.com/submissions/ MyPapers.cfm?partid=3621385.
- 12. Mondal D. Navigating knowledge in the digital era. Liva Press; 2025. ISBN: 9999327567, e-ISBN: 978-99993-2-756-5. https://elivabooks. com/en/book/book-4238987726. https:// www.amazon.com/dp/9999327567.
- 13. Mondal D. Innovating library futures: Metadata, technology, and the librarian’s role in educational transformation. 2025. e-ISBN: 978-99993-2-831-9. https://www.elivabooks. com/en/book/book-3705626088.
- 14. Mondal D. Transforming education through technology: Robotics, AI, teacher training, and policy implementation. 2025. e-ISBN: 978- 99993-2-835-7. https://www.elivabooks.com/ en/book/book-8583551325.
- 15. Dutta S, Mondal D. Virtual reference services: A changing trend of connecting users in a virtual learning environment. In: Strategies of Library Management in the Digital Era. Jaipur: Raj Publishing House; 2021. p. 280–7. ISBN: 978-93-88997-12-6.
Data Sharing Statement
Funding
Author Contributions
Ethics Declaration
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
About this article
Cite this article
Mondal D. User Perception of ChatGPT and Traditional Reference Services. Ind J Lib Inf Sci. 2025;19(3):209-13.
Licence:
Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.
| Received | Accepted | Published |
|---|---|---|
| July 24, 2025 | September 05, 2025 | December 25, 2025 |
DOI: 10.21088/ijlis.0973.9548.19325.1
Keywords
Artificial Intelligence (AI)ChatGPTReference ServicesUser PerceptionSearch for Similar Articles
Similar Articles
- Literature Review: A Historical Overview of the Open Access Movement
- Literature Review: A Historical Overview of the Open Access Movement
- How accurate are cited references in Management journals?
- The Impact of Open Access Movement on Science and Communication Researchers: A S...
- Connecting the Dots: Indigenous Literature and Digital Learning Platforms
Article Level Metrics
Last UpdatedSaturday 07 February 2026, 13:06:18 (IST)
Accesses
Citations
Download citation
Article Keywords
Keyword Highlighting
Highlight selected keywords in the article text.
Timeline
| Received | July 24, 2025 |
| Accepted | September 05, 2025 |
| Published | December 25, 2025 |
licence
This license enables reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator.